Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

γ-Aminobutyric acid (4-Aminobutyric acid) is the predominant inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $43 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $58 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $93 | In Stock |
| Description | γ-Aminobutyric acid (4-Aminobutyric acid) is the predominant inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. |
| In vitro | γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) functions primarily as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mature central nervous system. The addition of GABA into the cell culture medium promoted the proliferation of GABRP-expressing PDAC cells, but not GABRP-negative cells, and GABAA receptor antagonists inhibited this growth-promoting effect by GABA. The HEK293 cells constitutively expressing exogenous GABRP revealed the growth-promoting effect of GABA treatment. GABA treatment in GABRP-positive cells increased intracellular Ca2+ levels and activated the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/Erk) cascade[1]. GABA exerts antidiabetic effects by acting on both the islet β-cells and immune system. Unlike in adult brain or islet α-cells in which GABA exerts hyperpolarizing effects, in islet β-cells, GABA produces membrane depolarization and Ca2+ influx, leading to the activation of PI3K/Akt-dependent growth and survival pathways[2]. |
| In vivo | GABA is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the adult brain that has a parallel inhibitory role in the immune system. GABAergic medications are used to treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, epilepsy, and to induce sedation, and anesthesia. GABA is neuroprotective in animal models of stroke. GABA treatment decreases inflammatory cytokine production in peripheral macrophages. It decreases T cell autoimmunity and the development of inflammatory responses in the nonobese diabetic mouse model of type 1 diabetes[3]. In the adult brain, GABA induces a fast inhibition in neurons mainly through the GABAA receptor (GABAAR). GABA is produced by pancreatic β-cells. GABA released from β-cells can act on GABAAR in the α-cells, causing membrane hyperpolarization and hence suppressing glucagon secretion. GABA-treated mice showed higher circulating insulin, lower glucagon, nearly normal glycemia, improved metabolic conditions, and maintained close to normal glucose tolerance during a period of 53 d after STZ injections[2]. |
| Cell Research | GABRP-positive cell lines, KLM-1 and PK-45P, and GABRP-negative cell lines, PK-59 and KP-1N, are incubated with GABA or GABA receptor agonist Muscimol at serial concentration (0, 1, 10, 100 μmol/L) in appropriate medium supplemented with 1% FBS for 6 days. To inhibit the GABA-mediated pathway, cells are incubated with 250 μmol/L of GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline methiodide or 1 mmol/L of GABAB receptor antagonist CGP-35348. After 6 days of exposure to either of these drugs, cell viability is measured by MTT assay as described above.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Piperidic acid, Gamma-aminobutyric acid, 4-Aminobutyric acid, 4-Aminobutanoic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 103.12 |
| Formula | C4H9NO2 |
| Cas No. | 56-12-2 |
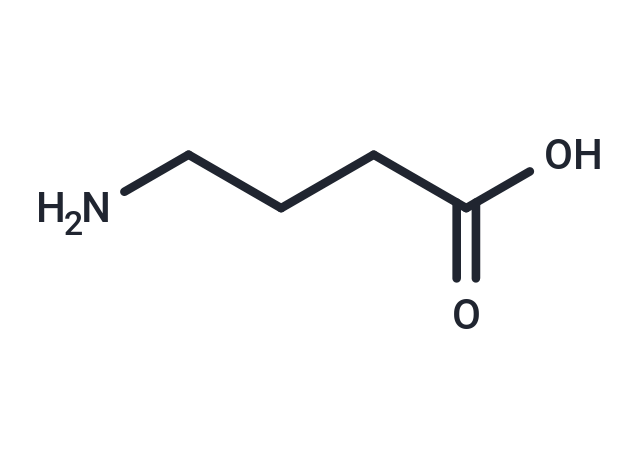
| Smiles | NCCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.11 g/cm3. Temperature:20 °C. |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 100 mg/mL (969.74 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: Insoluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.